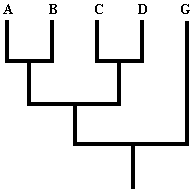
Phylogeny
Phylogeny: a) the relationship of organisms, usually presented as a branching diagram (Fig. 1) of the evolutionary pattern, and usually produced by a reproducible method (e.g., cladistics). Explicit hypotheses about a relationship. The 'best explanation of the available data', not the final truth!

Figure 1.
Character, character states: A character is a set of homologous features, sharing common origin, which can be described as separate entities, character states. Character states are mutually exclusive, and every organism in the analysis can have a state assigned, and every state evolved only once.
Cladistics: A particular branch of phylogenetic analysis, describing evolutionary patterns from parsimonious analysis of observed characters.
Phenetics: Originally (1960s) developed as a tool for taxonomy. Classification of organisms exclusively on 'numerical difference' (hence also known as numerical taxonomy), a calculated difference of measured or counted characters.
Techniques
Cladistics
Maximum Likelihood
Stratophenetics
'Back of the envelope'